Software Development Service
For several years, software development has become an essential aspect of business growth. Numerous studies and reports indicate that small and medium-sized French companies have fallen behind in their IT development. There are many practical applications of IT development within a company : management (financial, logistics), human resources, performance measurement, team monitoring, etc. The areas affected are varied and multiple.
Whether you are a VSE / SME, an association, a community or anyone wishing to gain notoriety or present products or services, IT development is necessary for the proper functioning of your structureand plays a major role in your reputation. A few examples: management of stocks, disputes, performance or resources… an adapted and efficient management software will only bring positive results and will have an important part in your growth. By giving you greater visibility and therefore a better understanding of your structure, you will be able to make the best decisions for it and therefore optimize your performance and profitability as much as possible by taking advantage of all the power of software computer and web and mobile applications can deliver.
With the competition, any organization, whatever its size, must be equipped with a modern and efficient computer system and software. Incite Software Pvt. Ltd. offers to support you by putting its team of qualified developers at your service in order to offer you a complete and tailor-made solution for each of your needs.
Internet of Things (IoT): Applications for everyone
There are many applications of the Internet of Things. This ranges from IoT for the consumer and business IoT industries to manufacturing IoT as well as industrial IoT (IIoT) . These applications cover many verticals, including automotive, telecommunications and energy.
The IoT (Internet of Things, for Internet of Things) is a system of interconnection between computing devices, machines, objects, animals and even people, provided with unique identifiers (UID) with the ability to transfer data over a network. And without human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction. Thus, it may be a person with a heart monitor implant or a farm animal equipped with a biochip transponder .
Or an automobile equipped with built-in sensors to warn the driver when tire pressure is low. Globally, it is any natural or artificial “object” to which an IP address can be assigned and which can transfer data over a network. More and more companies, regardless of industry, are using IoT to operate more efficiently and better understand their customers, in order to provide better services. But also to improve decision-making and increase the value of the company.
An IoT ecosystem is made up of smart, web-enabled devices. They use integrated processors, sensors and communication hardware. This allows them to send and collect data, but also to process the data they acquire in their environment. They do this by connecting to an IoT gateway or other device. As for the data, they are either sent to the cloud or analyzed locally.
All of these devices communicate with each other and act on the information they get from each other. They do most of the work without human intervention, although operators can interact with them, including installing them, giving them instructions or accessing data. As for connectivity, networking and communication protocols used, they depend on the specific IoT applications deployed.
According to many consulting firms, the future of the IoT market remains bright, despite the concerns it raises. Thus, Bain & Company expects the sector’s annual revenue to exceed $450 billion by 2020, while Gartner expects 20.8 billion connected objects at the same time. The IHS Markit firm estimates that the number of connected objects will increase by 12% per year, to reach 125 billion by 2030. Finally, McKinsey & Company estimates that the IoT will have an impact of 11.1 trillion dollars. ‘by 2025.
Big-Data Analytics
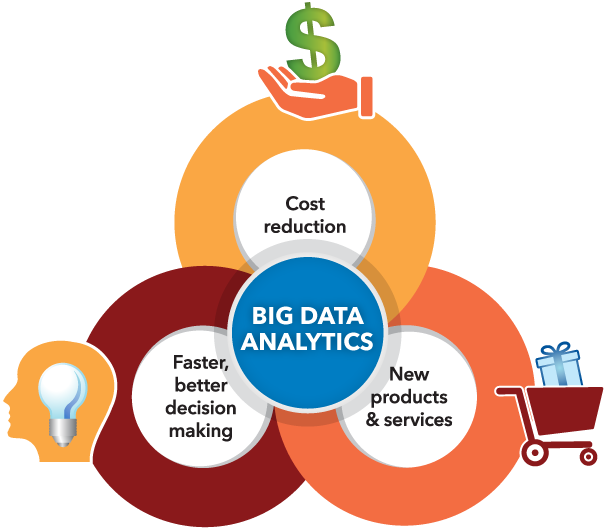
The definition big data arises from the fact that the current already substantial amount of data will multiply in the future , examples of big data come from IoT devices – Internet of Things as well as from smart cars in circulation, but also from the use of social networks and etc.
Data sources are many and constantly increasing and therefore what characterizes big data is not only the quantity , but also the complexity due to the variety of data types that can be recovered.
The concept of big data implies several factors, from the infrastructure necessary to collect and archive them, to the tools to analyze them up to the skills necessary to manage them, starting with big data analysts.
The definition of big data analytics refers to the process that includes the collection and analysis of big data to obtain useful information for the business. In fact, big data analytics techniques make it possible to provide companies with original insights, for example, on the market situation, on the competition, on the other hand on customer behavior on how to refine customer experience strategies and so on. To carry out the activities aimed at providing these and many other valuable information to improve the business activity, software (from databases and tools useful for acquiring and processing information to applications dedicated to specific business processes), services (for example, for customizing technologies and successfully integrating them into pre-existing systems) as well as, of course, infrastructural resources (computing capacity, storage, etc.).
It may seem obvious, but since it is the obvious things that are least thought about, the first question to be established is what business purpose the big data analysis project should serve. If this is not immediately clear, the risk, and it is a high risk, is that the IOC and IT go their own way creating a big data architecture that may work very well, but which is then not aligned with the needs of the business and enterprise. And this is because this is what data analysis is: in the science of data analysis it is the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming and modeling data with the aim of extracting information that suggests and supports strategic business decisions.
The use cases of big data analysis fall into three groups:
- Operational efficiency and risks. Much of the examples of big data analytics built or planned to be soon are about reducing risk in financial analytics . Other areas where efficiency and risk reduction count are asset management (with a tip in fraud analysis), personnel management and the supply chain, where big data applications for preventive maintenance emerge. A global approach to these problems must consider the sharing of data and the exchange of ideas with business partners, as well as the tracking of the results obtained from the actions taken following these analyzes, in order to start a virtuous cycle.
- Application security and performance. Predictive analytics and big data analysis on the functioning of IT serve to prevent problems in the provision of services and to monitor events to be able to respond to them in real time. The analysis models, which must be discussed with security and service managers, use data logs generated by servers and network devices to assess performance levels, find bottlenecks and so on.
- Knowledge and customer service. Solutions and applications for big data analysis are used for marketing and sales projects, for product development, but also for the optimization of the digital experience .
Cloud Computing- SaaS, PaaS, DaaS, IaaS, and more

Thanks to cloud computing, the world of services has changed. We are in the As a Service era but to choose you need to understand the key of the offer and the advantages. This in-depth guide explains what cloud computing is and then the meaning of Iaas, Paas, Saas, etc., that is, the difference between the various approaches of on-demand philosophies.
What is cloud computing? In a nutshell, it is a form of advanced technological outsourcing . In fact, in the second millennium, companies can entrust the management of one or more IT resources to a specialized provider which, from that moment on, are provided via the Web through an outsourcing contract. All this, without the company having to bear the costs of purchasing licenses or machines to take advantage of essential services for the business.
Thanks to the cloud, the supplier will maintain all the infrastructure necessary to manage and distribute the services on demand (on demand) and with a pay per use formula. The methods of use are established by contracts that provide for a certain fee, the amount of which is defined on a periodic basis or on a consumption basis. All with a subscription to certain service characteristics (SLA – Service Level Agreement) and security such as to guarantee business continuity.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is a software distribution model ( management , middleware, e-mail management programs, videoconferencing as well as CRM modules , Business Intelligence , HR management and so on) in which a manufacturer develops, operates (directly or through third parties) and manages a web application, making it available to its customers via the Internet . In this way, a company can access the various applications it has bought through a web interface or a customized interface and access methods as established by the contract.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
The term Platform as a Service (PaaS) means an offer in which the client company is guaranteed a platform that supports the development of cloud computing applications. The platform includes programming languages, libraries, services and dedicated tools, entirely developed by the provider. The elements that make up the PaaS allow you to program, test, implement and manage business applications without the costs and complexity associated with purchasing, configuring, optimizing and managing the basic hardware and software necessary for development activities.
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS)
The cloud computing service that offers IT a platform for integrating data, applications, services and processes. These are platforms that often have fewer features than on-premise ones, but are easier to use. They provide model-based development tools and a portfolio of pre-packaged integrations; in addition, more and more frequently, they integrate API management functions .
They are ideal platforms to support cloud to cloud and mobile to cloud integration . They provide simpler development environments than on premise ones, making it easier to achieve what we call ad hoc integration, i.e. the integration of specific projects.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
You can’t explain what Desktop As a Service (DaaS) is if you don’t first explain what desktop virtualization is. The service, in general, arises from the development of deduplication technologies that use a hypervisor, that is a technique that allows you to run multiple (virtual) machines residing on a (real) computer called a host. This allows you to store the configuration of a computer operating system as if it were a photograph (snapshot) which allows you to release the same type of configuration on one or more workstations in a few clicks without having to deal with long installations and manual configurations as it happens. with physical desktop workstations.
More specifically, there are two main virtualization technologies: VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) and DaaS (Desktop as a Service) . What are the differences?
While VDI is an in-house approach, where virtual machines are managed on a local server, i.e. internal to the company, DaaS is a service provided by a cloud provider. In this way, desktop management is transformed into a service that is contracted according to pay per use and on demand methods. This significantly changes governance because it relieves the company of any management burden, freeing up resources and ensuring, at the same time, a state of the art infrastructure.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
The IaaS is a out osurcing evolved of all ICT resources. In the meaning of cloud computing, today we mean a group of technologies now so mature that it is possible to move anything on the cloud: the principle, in fact, is that thanks to a new generation software programming, physical resources (any physical resource) are transformed in a logical resource. So you can software servers, storage, appliances, switches, security devices, firewalls, routers and so on. Today, providers have come to be able to offer a large part of the network in the cloud: in practice, an entire virtual data center can reside on the cloud. This, in short, is the meaning of Iaas – Infrastructure As a Service (IaaS).
Hybrid Cloud
The definition of hybrid cloud provided by Gartner refers to a coordinated and “policy-based” way of managing, using and provisioning IT services within a set of internal and external cloud services.
The decision to move one or more data center resources to the cloud and have them managed by a provider on a public or private network, or to own the management (always deciding whether to use a public or private network) is only a question of needs analysis. .
In this case, you can opt for a hybrid cloud . What does it mean? The hybrid cloud is linked to the fact that the very nature of virtualization technology allows you to move resources to the cloud or back to the company at any time in an absolutely dynamic way. This means that virtual machines and associated workloads, as well as network resources or storage space can be brought back to them by restoring a previous configuration of the cloud computing infrastructure.
What does XaaS mean? From the cloud to Anything As a Service
What does Anything as a Service consist of? Basically, this is what XaaS is: it is an integral part of a holistic vision of those who trust and rely on cloud computing. This is the maximum evolutionary horizon in the curve of services offered in the cloud and is part of a development associated with the Internet of Things that is advancing at the pace of a prevailing smartification of objects. Managing platforms capable of administering, monitoring and securing all the sensorized objects of which public and private companies are dotting the world is a further challenge that cloud computing is very happy to welcome.
The difficulty is to find prepared providers with big shoulders, able to understand what is the analysis to be done to manage all the resources necessary to make the IOT work . Xaas is in fact the infrastructural side of the coin, supporting that Internet of Everything predicted for some years by a brand among the greatest Lords of Networking .
XaaS thus becomes the umbrella of all the above service models: SaaS, PaaS, Daas, and IaaS, in all its forms (Storage as a Service, Data Center as a Service, Disaster Recovery as a Service and saying).
What does multi cloud mean? The advantages of a correct cloud management strategy
Multi-cloud means the simultaneous use of two or more cloud services to minimize the risk of extensive data loss or downtime caused by localized component failures in the cloud computing environment, which can occur at the hardware, software or computer level. infrastructure. A multi cloud strategy allows to avoid ‘vendor lock-in’ situations and to use different infrastructures to meet the needs of different partners and customers.
OpenStack- Advantages and limitations
OpenStack is a combination of open source tools that uses virtual resources to create and manage public and private cloud computing . Such tools, or even features, are called projects. OpenStack projects sometimes proceed at development or debugging rhythms that are not perfectly synchronized with everything else (the different features are made available as they are developed so that debugging is almost always necessary).
OpenStack is now particularly attractive, both for end users and for vendors, as the maturity reached by the technology balances the fragmentation of the projects that compose it. The latest releases offer virtually everything needed to implement an IT infrastructure geared towards meeting the most emerging use cases of cloud computing.
One area in which OpenStack still shows gaps to be filled is that of serverless computing , a model in which the cloud computing platform allocates computational and storage resources to run an application, without developers having to worry about management anymore. relationships with operating systems and their dependencies.
DevOps: What is it?
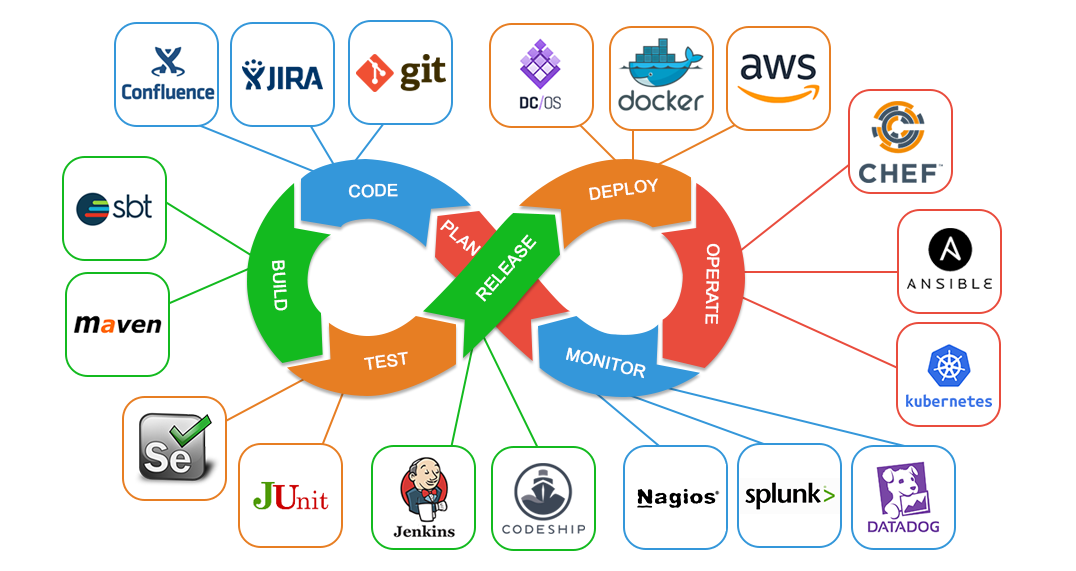
DevOps is a cultural and professional movement that emphasizes communication, collaboration and integration between software developers and IT operations professionals . It aims to create a culture and an environment in which software design, testing and release can be done quickly, frequently and efficiently. With improved workflow, DevOps can give organizations the flexibility to change faster, without sacrificing the quality and reliability of IT services.
Despite its name, DevOps doesn’t just appeal to software developers and IT operations professionals.
In fact, ‘ Dev ‘ indicates all professionals involved in the development of software products and services(including business representatives and suppliers) and ‘ Ops ‘ includes all professionals involved in the delivery and management of those products and services (including suppliers).
The DevOps movement has produced, and continues to produce, numerous principles that can be adopted by organizations of all sizes. All these principles have given rise to an approach that aims to improve the way in which the business provides value to its customers, suppliers and partners: DevOps certified professionals meet these skills thanks to greater skills and better communication and collaboration between IT teams.
8 benefits of adopting the DevOps methodology
- Improvement of the quality of codes, products and services (fewer failures, higher change success rate, etc.)
- Increased effectiveness (e.g. more time spent on activities that create added value, greater added value for the customer)
- Time to market improvement
- Better IT alignment and business responsiveness
- Faster, smaller and more frequent releases
- Less waste and fewer anomalies
- Productivity improvement, customer satisfaction, staff satisfaction
- Lower long-term costs
Our Expertise
Our in-depth knowledge of organizations and the expertise of our core business allow us to analyze your issues with discernment and responsiveness, and thus offer you personalized and feasible advice.
Incite Software Pvt. Ltd. supports you in the realization of your strategic and operational projects by offering you interventions with rigor and professionalism.
Our know-how and our expertise are recognized and recommended by our clients, who particularly appreciate our professionalism and the relationship of trust that we establish.
Our expertise in the medico-social, social and health sector makes us the ideal service provider who will understand you and support you in the success of your projects.
